November 18, 2025

The financial system has ceased to be a closed territory. The question is no longer whether a company can offer financial services, but rather how it will do so without wasting time, money, and sanity building an entire bank from scratch.
It is in this context that Banking as a Service providers have become central players. They provide the infrastructure that allows any company to launch digital accounts, cards, payments, international remittances, investments, and even crypto solutions in a modular way. All through APIs, clear documentation, and a regulatory base that handles the requirements with supervisory bodies.
In 2026, the question that really matters is not what BaaS is. The key question is: which providers are mature enough to withstand the pressure of a multi-currency and multi-market world, with increasing demands for compliance, experience, and scale.
This article addresses this with three very practical goals: to explain the role of Banking as a Service providers, to show what has changed by 2026, and to position Azify within this global scenario of pluggable infrastructure.
What are Banking as a Service providers?
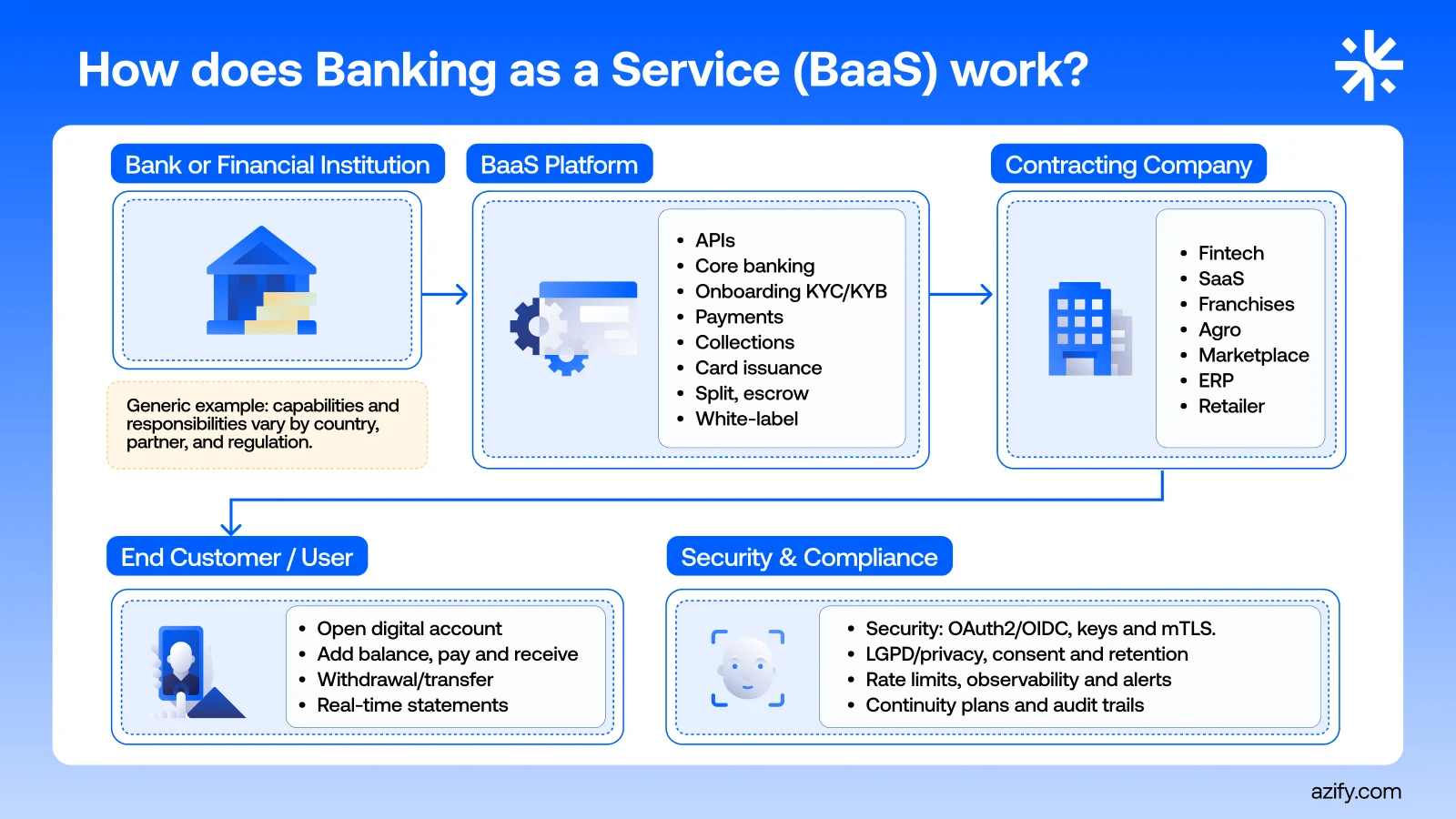
A provider of Banking as a Service is the company that provides the necessary infrastructure layer for other businesses to offer financial services to their customers without having to set up their own bank.
In practice, this provider takes care of everything that is heavy.
Connection with licensed financial institutions.
Regulatory layer, compliance, AML, and KYC.
Core of accounts, transactions, balances, and reconciliation.
APIs, SDKs, and technical documentation.
Risk monitoring, audit trails, and anti-fraud.
The provider's client focuses on user experience, product strategy, and market relationships. The BaaS provider focuses on ensuring that the financial engine behind all of this works securely, regulated, and scalably.
In the case of Azify, BaaS is an infrastructure that enables the offering of digital accounts, cards, payments, collections, remittances with global liquidity, and integration with investments and crypto, always from a compliance engine that is already embedded in the product.
Why did companies migrate to BaaS?
If you look at the curve of the last few years, you will notice a simple pattern. Fewer and fewer companies want to operate banking infrastructure in-house. Instead of hiring huge teams to build core banking, maintain compliance teams, and deal directly with all regulatory details, it is more efficient to use a Banking as a Service provider and focus on the business front.
The most common reasons are these.
Reduction of time to launch products. The time drops from years to months or weeks.
Less initial investment in heavy technology, infrastructure, and specialized teams.
Immediate access to mature functionalities, such as account accounting, reconciliation, audit trails, and anti-fraud.
Ease of testing new products, markets, or revenue models without rebuilding everything.
Possibility to operate in multiple currencies, including crypto liquidity, without multiplying complexity.
In practice, Banking as a Service providers have become the equivalent of vertical financial clouds. You do not buy the server. You consume the capacity on demand, with ready-made layers of security, governance, and scalability.
How does the architecture of a Banking as a Service provider work?
The majority of mature providers follow an architecture that can be summarized in blocks.
Core Banking and Accounting
This is the part that manages accounts, balances, transactions, reconciliation, ledgers, and transactional records. Without this, there is no bank.
Regulatory and Compliance Layer
This includes KYC and KYB, AML, sanctions lists, rules engines, alert management, audit documentation, and integration with regulated partners.
APIs and Documentation for Developers
This is the entry point. These are the endpoints that allow creating accounts, issuing cards, initiating payments, generating charges, triggering remittances, and checking risk. In a modern BaaS, this layer comes with strong authentication, encryption, and support for high transaction volumes.
Backoffice and Operational Tools
It’s not enough to just have an API. It is necessary to have backoffice for internal teams to manage accounts, monitor risk, follow the operations desk, and resolve exceptions. Azify, for example, highlights backoffice for accounts, onboarding, operations desk, and risk monitoring all in one place.
Special Integrations Layer
This includes components such as crypto liquidity, tokenization, gateways for exchanges, connections with card issuers, payment networks, and investment partners.
This arrangement enables something powerful. The company that hires the BaaS chooses which blocks it wants to activate and builds its product as if it were a financial lego.
Types of Banking as a Service providers
Not all BaaS providers are the same. In 2026, at least four main profiles can be seen.
Licensed banks that operate as a platform. These are traditional financial institutions that have decided to open up via APIs and offer their license and infrastructure as a service to fintechs, retailers, and digital platforms.
Technology companies with banking partnerships. These are companies that do not have their own banking license but integrate one or more partner banks and focus on developer experience, product, and programmable compliance. Azify is in this group, acting as infratech that organizes the entire regulated layer through authorized partners and delivers it via modular products.
Core platforms focused on digital banks. These are solutions more geared towards those who want to set up a complete digital bank, with their own app, but using a third-party core.
Niche specialists. Providers that focus on specific things, such as only issuing cards, only payment accounts, or only managing collections.
When you think of Banking as a Service providers for a multi-currency world with integrated crypto liquidity, it becomes clear that only the most complete and modular models can handle the task.
Global overview of Banking as a Service providers in 2026
Azify: reference in modular and multi-currency BaaS in Latin America
Among the Banking as a Service providers in 2026, Azify stands out right from the start. It combines the role of technological infrastructure with that of a translator of innovation in regulated markets, initially focused on Brazil with a vision for global expansion.
The Azify BaaS model relies on some key pillars.
Pluggable infrastructure with compliance engine
Azify structures its BaaS as a modular infrastructure, where each component is already connected to KYC, AML, auditing, and logging processes. This reduces the effort for the client, who does not need to redesign compliance flows with each new product.Banking for digital accounts for individuals and businesses
The banking layer includes complete infrastructure for digital accounts for individuals and legal entities. These accounts can be used to structure digital banks, solutions embedded in niche apps, or B2B financial hubs, always supported by a single technology base.Physical and virtual cards with real-time fraud protection
Azify offers the issuance of physical and virtual cards, compatible with digital wallets, proximity technology, and real-time fraud protection. In addition to issuance, it manages printing, national logistics, and visual customization according to the client's brand.Recurring and one-time billing
The Billing module allows for the automation and centralization of recurring billing and one-time charges, with real-time reporting and simplified reconciliation. It is ideal for SaaS, marketplaces, and businesses with subscriptions or recurrence.Remittances with global liquidity
The Remittance module focuses on international transactions with global liquidity and integrated compliance. The combination of BaaS with other Azify products, such as Liquidity as a Service and integrations with crypto, allows for structured crypto liquidity and currency exchange, always in partnership with regulated institutions.Open APIs and developer experience
Azify's APIs are open, documented, and designed for product and engineering teams that need to integrate quickly and securely. The company treats DX as a central part of its value proposition.Integrated back office for accounts, operations, and risk
Azify delivers a back office that consolidates accounts, onboarding, trading desk, and risk monitoring into a single platform. This reduces operational chaos and aligns the product, risk, and customer service areas around the same data.
In practice, Azify positions itself as one of the most complete Banking as a Service providers in Latin America, with a clear differential: the ability to connect traditional finance to digital in a multi-currency and multi-market world.
Other global Banking as a Service providers
Alongside Azify, some global players have established themselves as references in their markets.
SDK.finance
White label platform for wallets, digital banks, remittances, and payment services, with modules and APIs that allow building everything from wallets to acquiring solutions.

Marqeta
Known for issuing cards and the ability to orchestrate payments in various countries from a single platform. Very strong in the fintech segment and customized card programs.

Solaris
Licensed bank that operates as infrastructure in Europe. It allows companies to create financial solutions using Solaris's own license, focusing on accounts, cards, and credit.

Galileo
Reference in APIs for cards, accounts, and payments, serving as the base for various digital banks and fintechs, mainly in North America.

Treezor and Intergiro
Strong in payment solutions, wallets, and modular banking services for European companies, focusing on speed of integration and scalability.

These providers helped create the first mature generation of global BaaS infrastructure. Azify emerges in a second moment, already born in the context of crypto liquidity, tokenization, and emerging markets, focusing on connecting this universe to regulated infrastructure.
How to choose a Banking as a Service provider
In light of this scenario, choosing a Banking as a Service provider has ceased to be a purely technical decision. It is a strategic choice that impacts product, compliance, risk, expansion, and brand position in the market.
Some criteria are indispensable.
Regulatory capacity
The provider needs to operate with duly authorized partners, with clear responsibility paths. In the case of Azify, for example, the opening and management of payment accounts and the investment structure occur through regulated partners, with well-defined roles.Functional scope
Consider what you need today and what you will need in two or three years. Accounts, cards, collections, remittances, crypto liquidity, investments, tokenization. The more you can cover within the same infrastructure, the less friction you will experience when growing.API quality
Documentation, examples, SDKs, sandbox. The developer experience needs to be treated as a priority, or the integration cost will skyrocket.Back office and operation
Check if the provider offers complete dashboards for internal teams. It is pointless to have excellent APIs if the risk and operations team struggles to see what is happening.Partnership culture
A good BaaS provider is not just an API supplier. They act as a product partner, helping to design journeys, flows, and business models.
Use cases of Banking as a Service providers
To visualize the impact, think of some practical scenarios.
A B2B services marketplace that wants to offer digital account, card, and billing for its providers, with integrated withdrawals, receipts, and international remittances.
A retail company that wants to create a loyalty program with a digital account, its own card, and financial benefits for high-frequency customers.
An investment platform that wants to combine traditional products, such as CDB and mutual funds, with crypto liquidity and tokenization of real assets, using Azify's infrastructure to connect the ends.
A foreign fintech intending to enter Brazil that needs a partner familiar with the local regulatory environment, offering payment accounts, cards, Pix, billing, and secure connections with crypto.
In all these scenarios, a well-chosen Banking as a Service provider can be the difference between a project that scales and one that gets stuck on operational issues.
Trends for the future of BaaS providers
Looking ahead, some trends seem inevitable.
BaaS increasingly combined with Liquidity as a Service and Investment as a Service, forming complete layers of pluggable financial infrastructure.
Growth of the regulated tokenization of real assets, with BaaS providers connecting the fiduciary world and the crypto world transparently.
Top Banking as a Service
Intensification of the use of artificial intelligence in fraud prevention, risk analysis, and compliance automation.
Top Banking as a Service
Opening of more markets for embedded finance, especially in sectors previously considered traditional, such as industry, agribusiness, and logistics.
Everything points to a scenario where Banking as a Service providers cease to be a differential and become basic infrastructure. The choice of partner will define who can innovate responsibly and who remains trapped in complexity.
Conclusion
Banking as a Service providers are the invisible foundation of the new financial economy. They connect businesses to the banking system in a modular, secure, and scalable way. In 2026, the game is no longer just about offering APIs. It’s about delivering a combination of infrastructure, programmable compliance, global liquidity, and real support for product, operations, and risk teams.
In this scenario, Azify stands out as a key player among Banking as a Service providers. With plug-and-play infrastructure, compliance engine, Banking modules, Cards, Collections, Transfers with global liquidity, integrations with crypto, tokenization, and investment products, it positions itself as one of the most complete options for companies looking to operate in a multi-currency and multi-market world.
If the future of finance is to be invisible, Banking as a Service providers are exactly that thread that stitches everything behind the scenes. And the decision about who will be your supplier is, in practice, a decision about what kind of financial future your company wants to build.



